When you open a website, your browser verifies its SSL/TLS certificate to assure that the connection is secure. If the certificate is valid, the website opens it with HTTPS protocol (Where ‘S’ stands for secure). However, if a browser detects any issue, it shows security error.
One of these errors is NET: ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID, which generally occurs when a common name on the SSL certificate does not match the domain name. This mismatch typically happens if the SSL certificate is not configured correctly, or if the domain has changed without updating the certificate.
This article covers the details of NET:ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID SSL error, how it occurs, and top tips to solve it. Read on to know more.
Table of Contents
What is NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID Error?
NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error takes place when the domain name a user is trying to access does not match the common name (CN) or any of the Subject Alternative Names (SAN) listed on the site’s SSL certificate. To understand this, you need to first understand the concept of a common name that applies to SSL certificates.
SSL certificates are issued to initiate HTTPS protocol, which is responsible for encryption functions. Through encryption, all communications and data transfers between web servers and browsers are secure and inaccessible to third parties. Certificate Authorities usually issue SSL certificates to specific domain names. If the specific domain name does not align (fails to match) with the issued certificate, the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error occurs. This explains why the error is sometimes called the ‘SSL common name mismatch error’.
NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID Error Across Different Web Browsers
1. Error in Google Chrome Browser
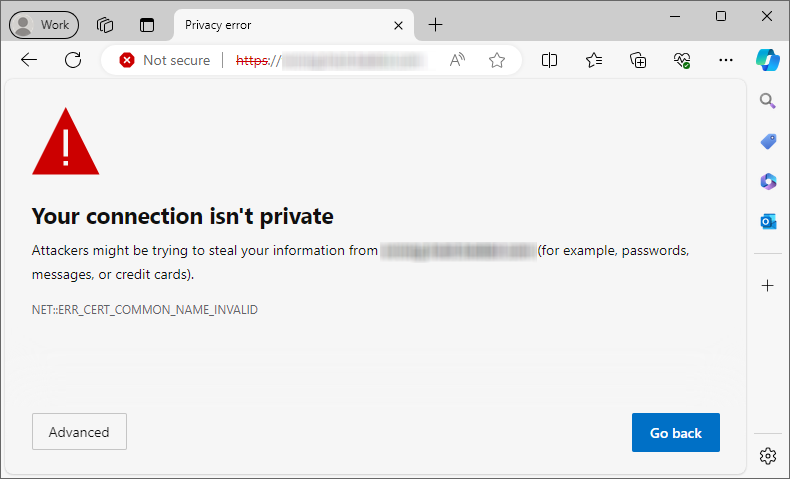
In Google Chrome, the message; Your connection is not private appears followed by NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID.
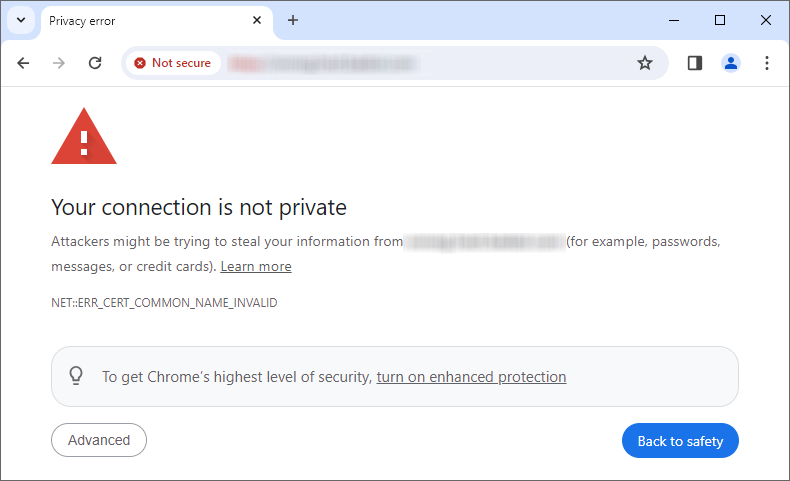
Additionally, the Chrome browser warns visitors that attackers might be trying to steal their information through the website. Chrome provides examples of such information, including passwords, messages, and credit cards. It also gives users an option to report such incidents to Google. Users can choose to exit the website or continue browsing by clicking on Advanced.
2. Error In Mozilla Firefox
The message; “Warning: Potential Security Risk Ahead” appears for Mozilla Firefox. The browser further tells users it has detected and cannot proceed with processing their request. It cautions users that proceeding to the site might lead to attackers stealing their information. Firefox gives examples of such information as passwords, emails, and credit card details.
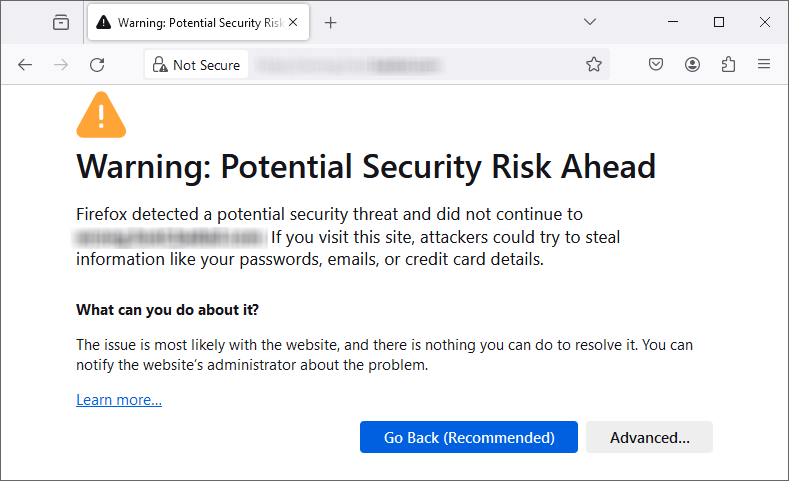 As you will notice from the screenshot above, Firefox does not show the code for the common name invalid error. Instead, the browser tells web visitors what has happened with their connection. Users can click on Learn more… to get solutions to the problem.
As you will notice from the screenshot above, Firefox does not show the code for the common name invalid error. Instead, the browser tells web visitors what has happened with their connection. Users can click on Learn more… to get solutions to the problem.
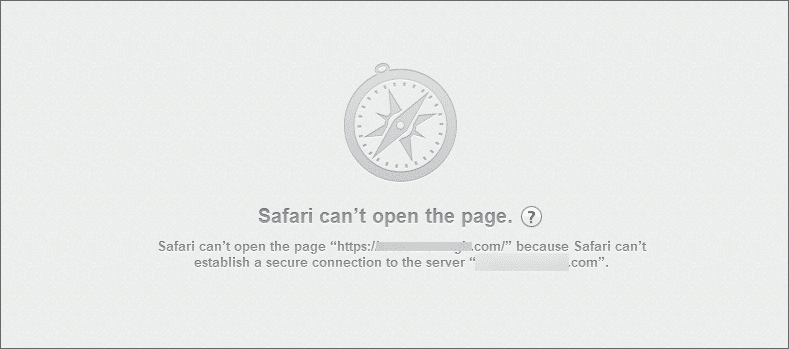
3. Error In Safari Browser
On the Safari browser, the error appears with the message: “Safari can’t verify the identity of the website.” This message is usually followed by the domain name of the website. See the attached screenshot:
4. Error In Microsoft Edge
When you get a “NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID” error in Microsoft Edge, a big red warning page pops up saying your connection isn’t private. It also shows a code (NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID) to help you fix the problem.
Common Reasons Behind the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error
NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error can be caused by several common issues related to the SSL certificate. It can be related to your domain configuration, expired certificate, or the way your certificate was issued. By understanding the main causes behind the error users can resolve it, and securely access the website without encountering this warning.
Let’s look into what are the common causes behind this error and how it impacts website security.
- Domain name mismatch: This is one of the most common reasons behind this error. When the certificate is issued to a specific domain name and the domain name does not match the issued certificate, the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error occurs.
- The SSL Certificate Issued To A Different Domain: If the SSL certificate is issued to a different domain, then using it on an alternative domain could result in an error. For instance, if a certificate is issued for www.abcde.com and you use it on www.12345.com, the error is bound to occur.
- Expired Certificate: An expired or misconfigured certificate could result in an error.
- Using a Non-Fully Qualified Domain Name: Using a non-FQDN, such as a local host or internet server name, could be the culprit causing the error.
- Interference from Third-party Browser Extensions: Extensions that manipulate internet connections, such as ad blockers, VPNs, and security plugins, could alter the certificate and cause a mismatch.
- Obstructions from Antivirus: Some antivirus software comes with advanced features, such as scanning HTTPS sessions. These features substitute the servers’ certificates with other certificates. This could cause a mismatch and interfere with the handshake process.
- Corrupted Browser Cache and SSL State: If you update your certificate but the browser still holds the old certificate in the cache, then a mismatch is bound to occur, and consequently, the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error.
How to Fix NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID Error?
At this point, it is crystal clear that many factors contribute to this error. This makes it difficult to narrow down to a specific cause and align a tailored solution. There are several troubleshooting solutions you can try out to resolve this error. This section covers the 12 most effective tips to fix the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error. Here’s how to check the Common name in Chrome:
1. Verify SSL Certificate Details
There is no doubt that the most common cause of the error is the mismatch between a website’s domain and a common name. To avoid this error, you must start by ensuring you install the right SSL certificate that aligns with your domain name. You should also configure the certificate appropriately. Here’s how to check the Common name in Chrome:
Step 1: Click on the tune icon on your website.
Step 2: A dropdown menu will appear. Click on connection is secure.
Step 3: Select Certificate is valid from the menu.
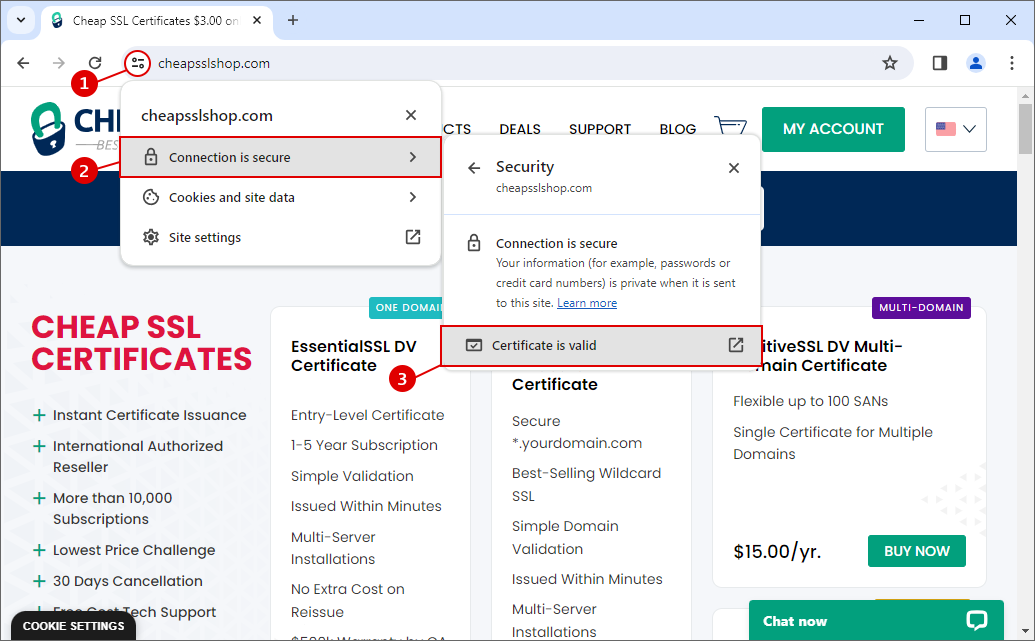
From here, make sure whether the actual domain name is in sync with the common name attached to the certificate. If they do not sync, it means there is a common name-domain name mismatch. You will need to install a fresh certificate.
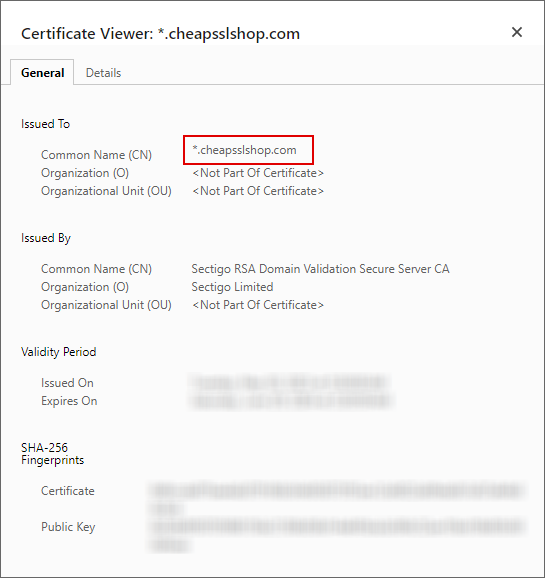
Wildcard SSL certificates are designed to encrypt data from multiple subdomains. So, if you have a wildcard certificate and have the NET: ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID_ERROR it means the certificate does not cover the subdomain you want to access. For instance, *.example.com will cover domain names such as blog.example.com, mail.example.com, etc. But it will not cover sub.mail.example.com You have to issue a different certificate for *.mail.example.com
For multi-domain (SAN) SSL certificates, you will have to dig deeper to verify the certificate. SAN certificates cover multiple domains within a website. The certificate covers top-level domain variations, www, non-www, and subdomains.
To verify the domains covered by the certificate, click on the certificate in your browser, open the certificate details, and navigate to Subject Alternative Name section. You can see all the domains that your certificate covers. Check that the domain you are trying to access is listed here.
2. Update Your Web Browser and Operating System
Updating your operating system and web browsers ensures software stability. Software and OS stability could help minimize a lot of errors including the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error.
Update Web Browser
Follow the steps below to check for updates in your browser (chrome).
Step 1: Click on the three dots in the top right corner. Hover to the Help bar and Click on About Google Chrome.
Step 2: The settings panel will open. From here, if there is any update available chrome will begin downloading
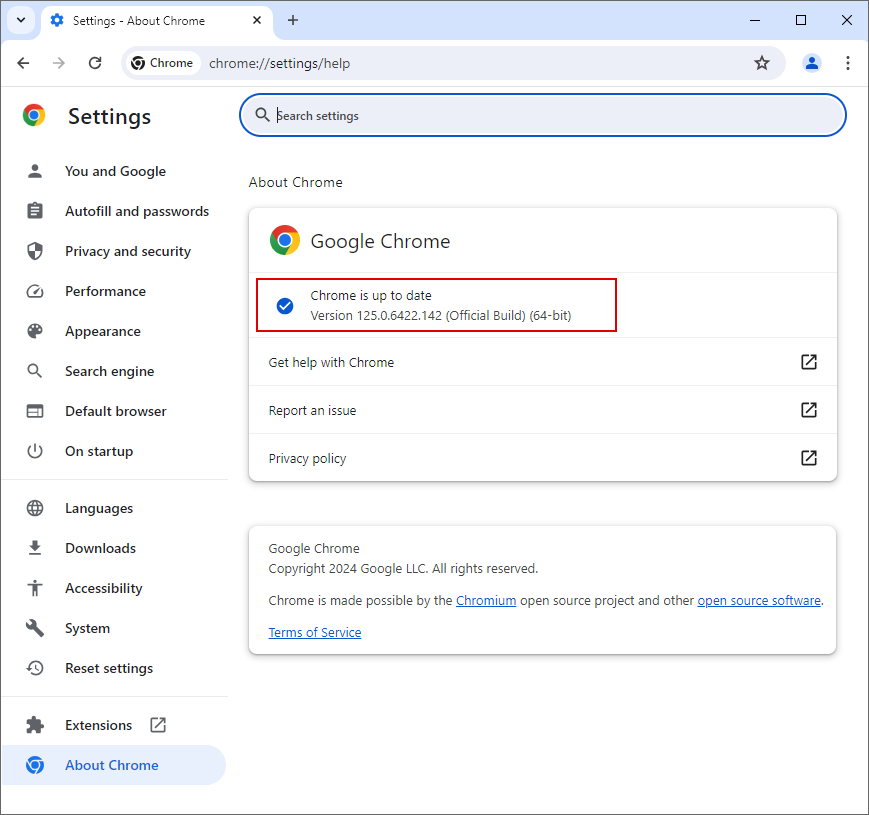 Step 3: Once the downloading is complete, there will be option to “Relaunch”. Click on it to update with the latest version.
Step 3: Once the downloading is complete, there will be option to “Relaunch”. Click on it to update with the latest version.
Update Operating System
For your operating system, you can follow these steps to update:
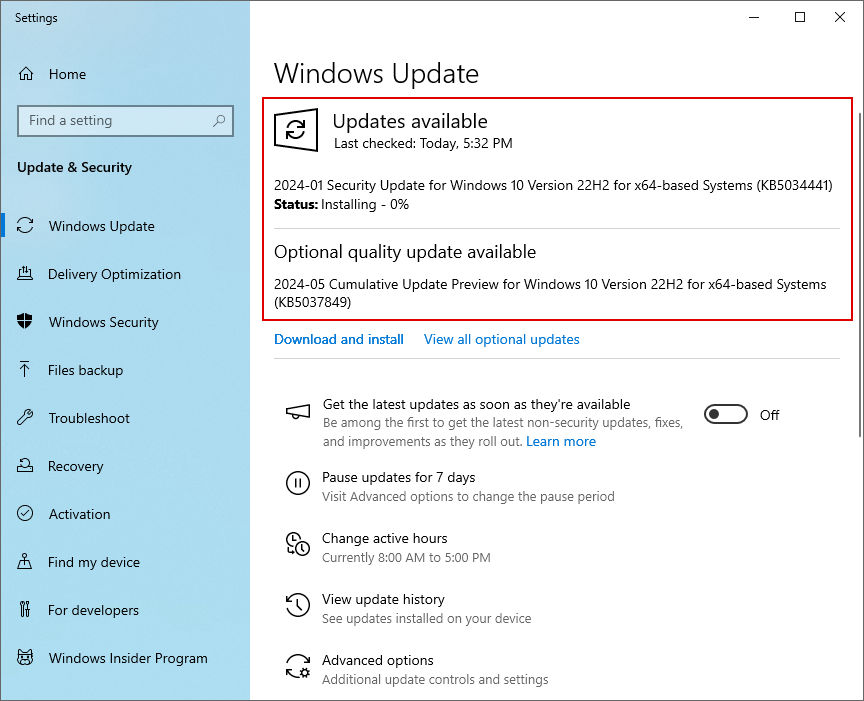
Step 1: Click on the Start bar on your computer and select Settings.
Step 2: From the settings panel, click on Windows Update. From here, you can proceed to check if your operating system is up to date. You can also download and install any available updates.
3. Check for Self-Signed SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are acquired from reputable certificate authorities. The certificate authority signs the certificate before issuing it to the users. That is not the case with self-signed certificates. Self-signed certificates are mere creations of users and are not issued by authorized CAs.
Self-signed certificates do not offer full encryption like that from CA-backed certificates. As such, most web browsers will flag websites using them as “insecure.” Some browsers may display the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error in cases of self-signed certificates. You can rectify the error by deleting the self-signed certificate and acquiring one from a reputable CA.
4. Check and Rectify All Misconfigured Redirects
Not all SSL certificates cover www and non-www domain variations by default. When you redirect your website from one server to another server without configuring certificate it causes error. So, before purchasing an SSL, you must check to ensure that it covers both domain variations.
To check the redirections of both, you can use several available tools. These tools check the redirect between www and non-www domain versions of your site.
Moreover, you can get a SAN (Subject Alternative Name) certificate that includes both domains and an extra certificate for the domain you’re rerouting from. To safeguard subdomains using wildcard domains, make sure you list them all rather than rerouting traffic between them.
5. Align Your WordPress Address and Site Address for Consistency
It is possible to mistakenly migrate your website’s address to HTTPS without an SSL certificate. This is a common occurrence in WordPress and could lead to the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error.
Fixing this is simple. Open your WordPress dashboard and go to settings. Click on General. Confirm whether your WordPress address URL and site address URL are similar.
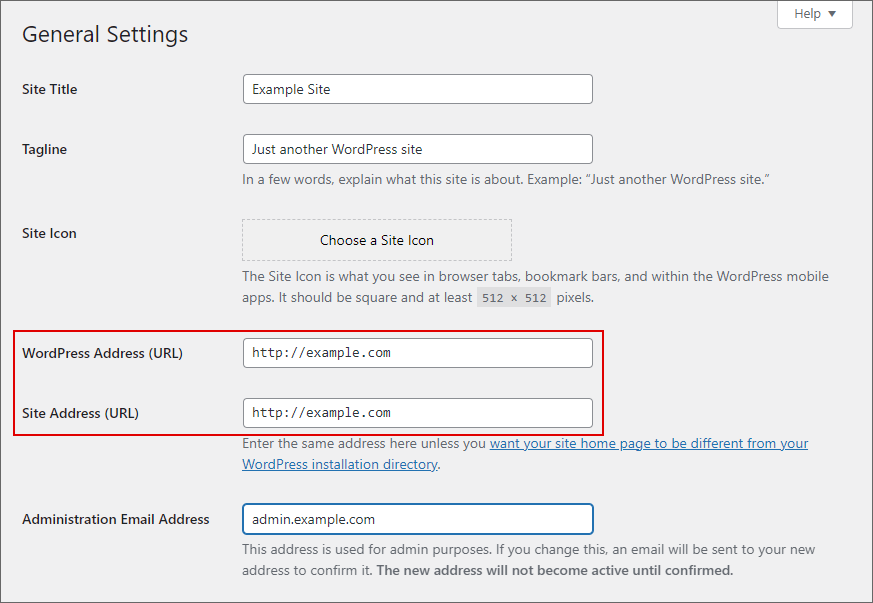
If the URLs use HTTPS in the absence of an SSL certificate, you will need to change them to HTTP.
6. Configure URL Settings In phpMyAdmin
NET: ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error can also cause because of URL variations between option_value in siteurl and home rows in your website’s database. In such a case, you will need to revise the URL settings of your WordPress. You can do so via phpMyAdmin. Here are the steps:
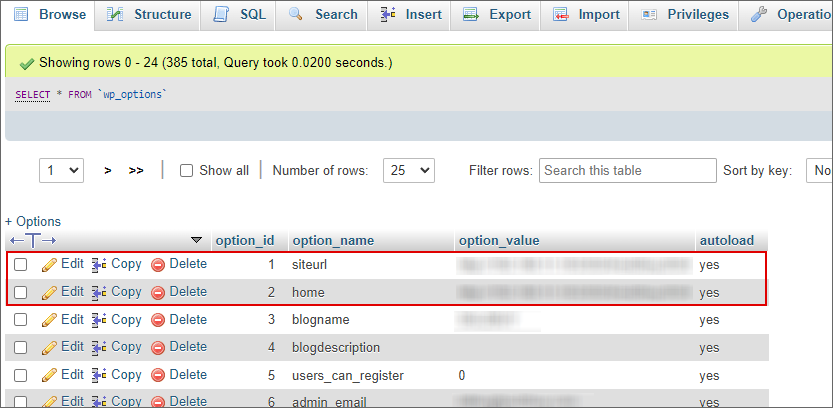
Step 1: Open phpMyAdmin application on your web hosting account.
Step 2: Select the database of your website and look for the wp_options table. Find the home and siteurl in the table and ensure they redirect to the same URL.
7. Clear Browser Cache and SSL State
An outdated cache might load an older website version, resulting in the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error. To prevent this error, you will need to clear the cache. Here are the steps to clear the browser cache in Chrome.
Step 1: Click on the vertical dots in the top right corner of the browser.
Step 2: Select Clear browsing data, alternately, you can press Ctrl+Shift+Del.
Step 3: From the dialogue box, select the time range with which you wish to clear data. Click on clear data.
In an attempt to speed things up, browsers might cache SSL certificates. The browser ends up failing to fetch the latest certificate version. This could result in an error. To resolve this on Windows OS, you will need to clear the SSL state. Here is how to do that:
Step 1: Search for Internet Options from the search button on the taskbar. Click enter
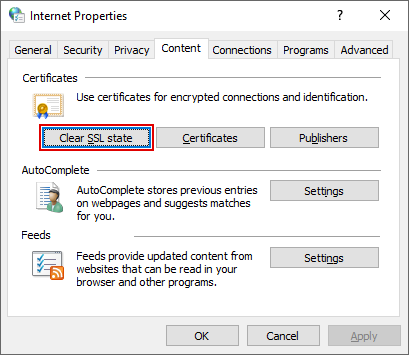
Step 2: Click on the Contents tab and then on the Clear SSL State option.
8. Temporarily Disable Antivirus or Firewall
Antivirus software comes with an SSL scanning feature. Such software might sometimes block users from accessing HTTPS websites, leading to an error. You should disable the antivirus software to resolve the error. However, you should only do so if you trust the website. Antivirus software is important, and disabling it could jeopardize website security.
Here is how you can disable antivirus software:
Step 1: Click on the Settings tab on the Start tab
Step 2: Go to Update & Security and then click on Windows security.
Step 3: Click on the Virus and Threat Protection tab. Navigate to Manage Settings. Find Real-time protection and turn it off.
9. Evaluate Your Proxy Configurations for Potential Discrepancies
Misconfigurations in the proxy settings can lead to restrictions on web access. This could cause SSL errors, including the NET:ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error. You will need to reset your proxy configurations to resolve the error. This process varies depending on the operating system you use.
Follow the steps given below to access proxy settings on Google Chrome.
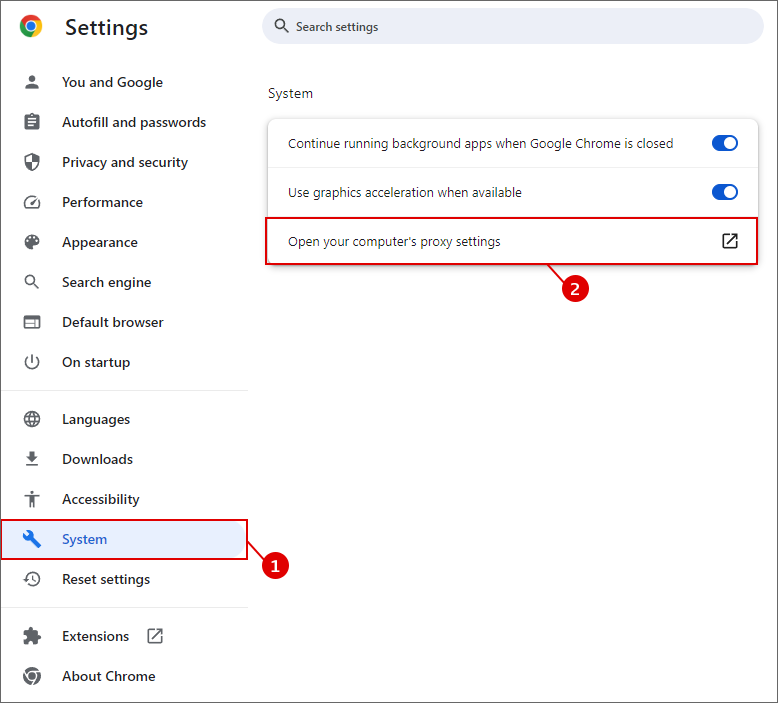
Step 1: Open Settings by clicking on the three dots in the top right corner.
Step 2: Click on System and click on Open your computer’s proxy settings.
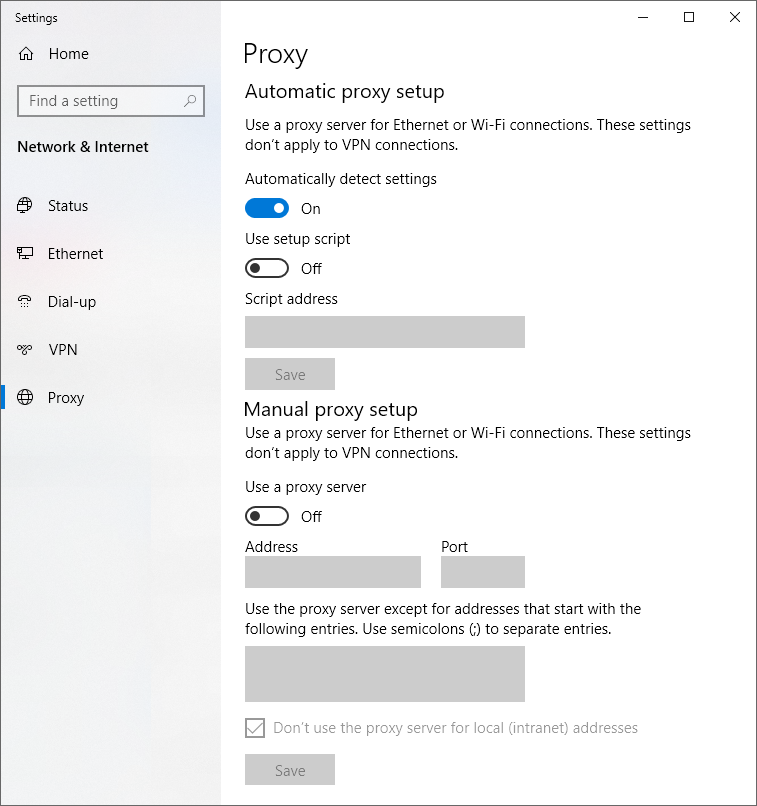
 For Windows users, the prompt will open the window for Proxy. You can proceed to alter the setting by clicking the option for Automatically detect settings.
For Windows users, the prompt will open the window for Proxy. You can proceed to alter the setting by clicking the option for Automatically detect settings.
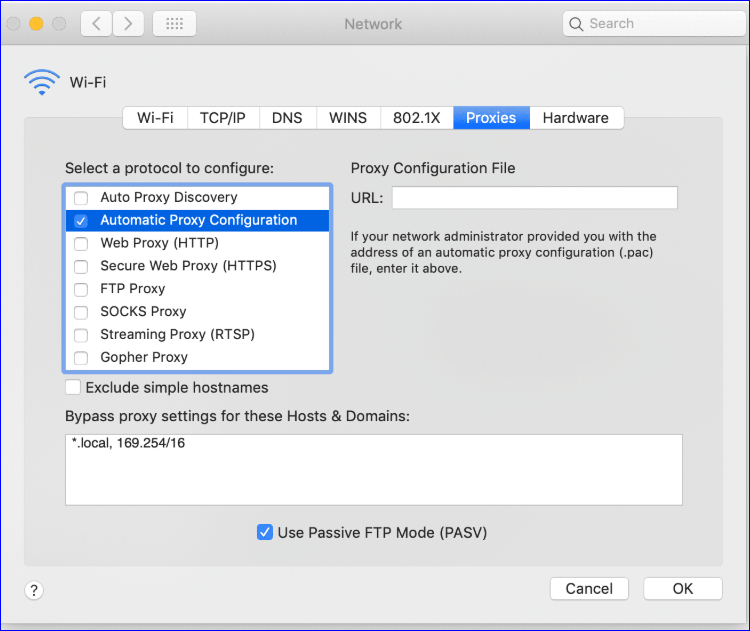
For Mac users, it will open your Network Settings window. Once open click on Proxies tab and then select Automatic Proxy Configuration.
After applying this step try accessing your site again, and check if the error is resolved or not.
10. Resolve Browser Extension Interference
Too many browser extensions might cause a host of issues due to extension conflicts. Such conflicts could lead to a common name mismatch, which results in the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error.
To check whether the error is a result of extension conflicts, try accessing it from incognito. If the website loads, the error may result from an extension conflict. To resolve this, you must disable extensions one after the other. If the site works in the absence of a disabled extension, then you must delete it. The extension is the culprit.
Step 1: Go to settings and click on Extensions.
Step 2: From the dropdown menu, click on Manage Extensions.
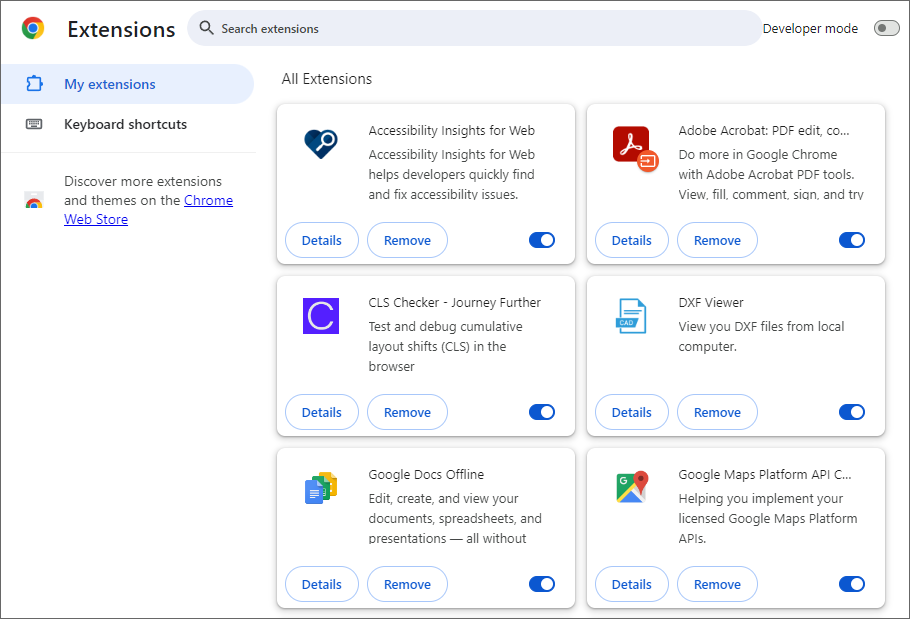
Step 3: Find the extension you want to remove and click on Remove.
11. Change Your LAN Settings
The purpose of proxy settings is to route web traffic. Routing helps to protect website visitors from hackers. Any proxy misconfigurations might result in SSL errors. You might have to change LAN settings to resolve such errors. Perform the following steps to change the LAN settings.
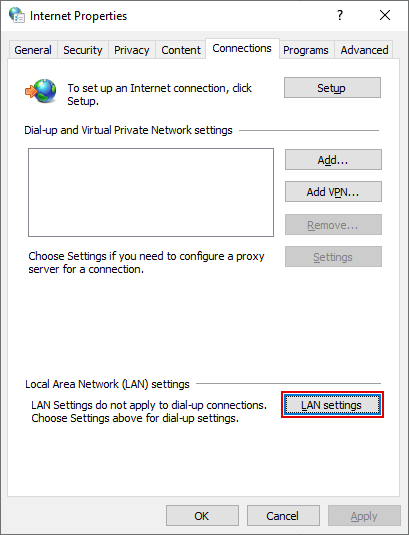
Step 1: Search for Internet Options from the search button on the taskbar. Click enter
Step 2: Click on the Connections tab and select LAN settings.
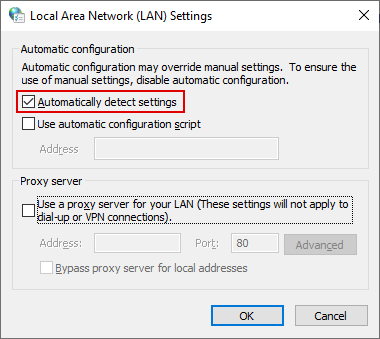
 Step 3: Ensure the Automatically detect settings box is checked. Save the changes by clicking on OK.
Step 3: Ensure the Automatically detect settings box is checked. Save the changes by clicking on OK.
12. Check Date And Time Are Proper
An incorrect date and time on your PC could result in the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error. Check to see if the date and time are proper. You can adjust the date and time by going to the Windows setting, selecting Time and Language, and the Date and Time.
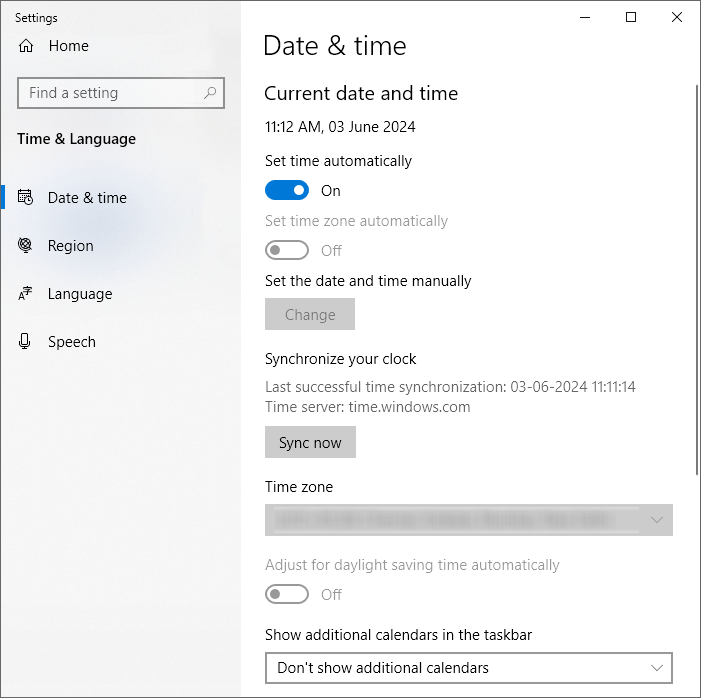
You can either choose to set it up automatically or manually.
If you use MacOS, you must follow the below steps
- Open the Apple
- Then go to System settings -> General -> Date & Time
- Choose the Set Date and Time Automatically Option
Effective Strategies to Prevent NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID Issues
Prevention is far better and cheaper than cure. Here are three key strategies to help you avoid the NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error.
1. Effective SSL Management
Most errors occur because of poor SSL management. Webmasters can do better to prevent this error by having effective SSL certification measures. For instance, you must always ensure the certificate is up-to-date. Ensure you renew your certificate before it expires. Automating the certificate renewal process could save you a big deal.
2. Proper Configuration
Your web server and SSL certificate should be properly configured at all times. Ensure the virtual host is properly set up. It is also wise to test the server compatibility with your SSL protocols.
3. Ensure Accurate DNS and Server Configuration
Ensure that the server configurations and DNS settings are correct and consistent with the domain names listed in your SSL certificate. Be sure to make regular checks to ensure your domain resolves to the correct server and that all subdomains are properly configured. Accurate DNS and server settings help maintain certificate validity and prevent errors.
Conclusion
The NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID error can be so frustrating. It can also be complex to fix, especially when you do not know what it is. You will need to narrow down and discover what is causing the problem. You should start by checking whether the common name in your certificate and the domain is the same. You can then move on to apply troubleshooting solutions covered in this article. The article has provided you with everything you need to know about the error. We hope it helps you solve the error.
Related Post: