This piece aims to offer a thorough understanding of HSM (Hardware Security Modules) and explain their role in safeguarding sensitive data.
Have you ever used a USB device to log in to your Windows PC or Google account? Then, you have experienced a hardware security module (HSM) without knowing it!
What is HSM? – A USB device that secures your data! Defining what HSM is in a few words does not justify its importance in your security key strategy. HSM provides cryptographic security with a robust hardware form factor, which is hard to break for cyber attackers.
This is why the HSM market size is growing at a CAGR of 16.2% and is set to reach $5.9 billion in revenue by 2033. Several factors contribute to a surge in the market size of HSMs and this article will focus on providing deep insights into all those aspects with benefits, challenges, best practices, and use cases.
Table of Contents
What is Hardware Security Module?
A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a physical computing device that provides secure key management and cryptographic operations. It protects and manages digital keys for strong authentication and secures sensitive data.
Businesses use HSMs to protect identities, transactions, and applications. They benefit from HSM’s capability to offer encryption, decryption, authentication, and digital signing services across diverse applications. Additionally, HSMs also guarantee compliance with cybersecurity laws by adhering to industry standards like FIPS 140-2 and Common Criteria.
The HSM serves as a Root of Trust within many organizations, being a dependable source in cryptographic systems. To enhance security, HSMs are typically kept off the organization’s computer network, requiring physical access for any potential breach attempts.
HSMs secure different data types like credit card numbers, images, code signing certificates, security keys, and videos. They can be in hardware form, or even cloud based.
What Different Types of Hardware Security Modules Exist?
There are two major types of HSMs used by various industries:
- General Purpose (GP)
- Transaction HSM
- GP HSM- General purpose HSMs generate cryptographic commands that are hard to break and ensure security for sensitive information. Businesses use GP HSM for secure symmetric key management, digital signature creation, support of public critical infrastructure (PKI), and even crypto wallets.
- Transaction HSM- These HSMs are also known as the payment HSM, which have more advanced modules than GP HSM. It secures payment card data and mobile apps and enables point-to-point encryptions.
How Do Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) Work?
HSM architecture contains several elements like an application or interface, an HSM client API library, a storage controller, and an HSM storage device. The core HSM product may be a network-enabled service with a token for all the database replicas. Client API library implements PKCS#11, allowing different databases to support HSM products.
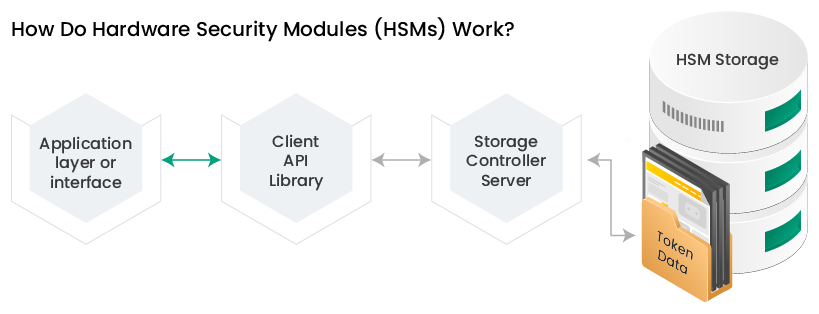
A storage controller communicates with the client API library and manages the data token. Every HSM stores a replica of the data as an encrypted token, further decrypted through a user account pin known as a token identifier.
HSMs ensure only the intended user accesses the information stored in it through cryptographic encryptions. This is why it is also used for security key generation and management.
Cryptographic key generation and management with HSM
Hardware security modules secure cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle. Every cryptographic key has different phases in its lifecycle, from generation to destruction. HSM enables the management of keys through,
- Provisioning where HSM creates keys using a TRNG
- Stores and backup keys
- Installs keys in a cryptographic device
- Manages keys through encryptions
HSMs secure the entire lifecycle, beginning from key generation through TRNGs or True Random Number Generators. These random numbers are based on physical entropies like avalanches or thermal data. Random numbers act as a seed to generate secure cryptographic keys.
If the random number generator is weak, security can be compromised. Businesses prefer hardware-based TRNGs because they are more robust than software-based random number generators.
HSMs act as a secure backup for data recovery by companies and manage cryptographic keys. Due to strict design requirements and compliance with FIPS 140-2 standards, HSMs offer tamper-proof security for cryptographic keys.
However, the security of cryptographic keys is not the only benefit of using HSMs because it allows organizations to execute functions in a secure environment.
HSMs and secure execution environment
A secure execution environment will enable programs to run in a secure and isolated environment. HSM provides security to program executions through cryptographic encryptions. A regular execution environment (REE) uses HSM to encrypt or decrypt information as per functional requirements.
For example, if the specific task in REE has data, it will use HSM to encrypt the data and send it back to the issuer of functions.
Key Features and Capabilities of HSMs
HSMs are unique to many other security solutions due to cryptographic encryptions. It allows HSMs to secure data and security keys like no other solution. However, there are software-based options, but if you are looking for a robust solution, a hardware security module is the best option.
Some key features and capabilities involve:
Security key provisioning
HSMs can provision key generation without an algorithm. It uses TRNGs, which are used to crack and improve security for businesses. Provisioning also allows firms to generate keys for different purposes like validating transactions, identifying an app publisher, or authenticating data access.
Tamper resistance
HSMs provide tamper-proof security for your data. Compared to other security measures, HSMs have tamper resistance due to cryptographic encryptions, which are hard to overcome for any cyber attacker.
Cryptographic acceleration
Faster operations require hardware-based accelerations, and that is where you can use HSMs. It offers cryptographic accelerations, in which the encryption-decryption process makes data transmissions faster, reducing authentication overload.
Compliance support
HSM provides data security, ensuring compliance with crucial information regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Knowing the features and key management capabilities, deciding whether to use HSM for your systems becomes easier. However, understanding the use cases of HSMs becomes vital to maximize security using this security option.
Critical Use Cases for HSMs
From financial institutions to telecom companies and government authorities, businesses across domains use HSMs with varying use cases.
Banking and Finance
Financial institutions like banks, fund management, and insurance companies can use HSMs to secure transactional data. Such organizations can leverage the high security of HSMs to secure the financial data of users, access information for key stakeholders, and transaction logs. Finance companies can also use HSMs to secure keys, which enables access to root admins for the system.
eCommerce business
ECommerce businesses process millions of transactions and need to process user’s financial information. It also stores and analyzes user data, which requires security according to the PCI DSS standards for different financial institutions and eCommerce businesses.
ECommerce businesses can use HSMs to secure critical financial information like credit cards, debit cards, and credentials for online wallets.
Telecom companies
Network security is a significant concern for telecom companies, and HSMs can help secure customer communications. Securing the networks and communications also includes ensuring phone call encryptions. HSMs can help telecom companies secure calls, authenticate subscribers, and restrict access to the network.
Government and military
Government authorities need to store data from a large population across the country, which is where HSMs can be helpful. Authorities can use HSMs to store data securely and all the information on government transactions.
Retail stores
Retail companies handle millions of transactions regularly, both digital and in cash. HSMs don’t just help retail companies secure digital transactions but also all the records of cash transactions. Retail companies can also store digital certificates and encrypted financial data of customers on HSMs for enhanced security.
Healthcare business
Healthcare organizations and businesses use HSMS to store sensitive patient data, making it accessible for doctors and other professionals. HSMs are also vital to hospitals or other healthcare organizations for securing transaction data.
Cloud Computing
HSMs help secure cloud data through cryptographic keys by ensuring sensitive data runs within specific boundaries. This ensures that cloud data is secure across multiple environments due to particular limitations.
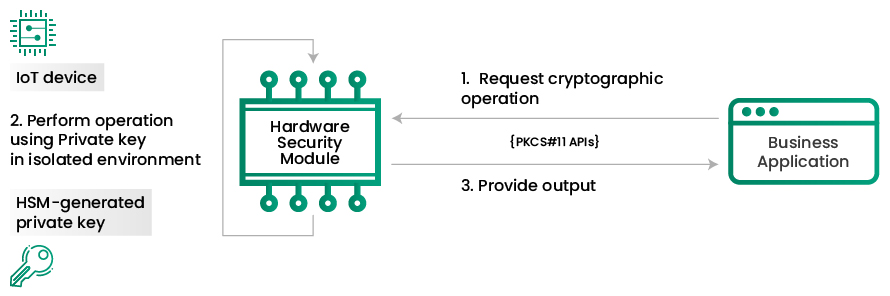
IoT (Internet of Things)
Hardware security modules provide secure IoT devices through entropy-based random key generation and secure vault. You can connect it with the machines and implement cryptographic operations on the IoT chip. HSMs also help improve the security of the nonvolatile memory of IoT chips.
While advanced features, capabilities, and use cases of HSM make for an attractive option, there are more benefits.
Benefits of Using HSMs
Your security strategy needs HSM inclusion due to its capabilities of securing sensitive data and critical management. A key advantage of HSM in security strategy is tamper-proof features. HSMs are best when transferring data across environments or embedded machines. It will protect data from leakages, enhancing the security strategy.
Especially if you are operating in a highly regulated industry like the banking sector or eCommerce business, HSM has several benefits. For example, it helps you comply with data regulation standards.
HSMs also help you save more on the cost of key management and security. It allows you to maintain security along the key management lifecycle, making sure there are no expenses on data recovery or leakages. For example, if you use HSM, data recovery becomes easier as it is a backup for many systems.
There are many benefits to HSM, making it a necessity for many businesses, but it is full of challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
HSMs do provide key management, but when you need to prevent malicious key usage, controls are limited. There are no mechanisms to detect misuse of security keys and no authorizations. This leads to security issues for businesses and leakages of administrative data.
Apart from the challenges of key abuse, HSMs also have limitations in hardware. So, if you are dealing with high data, security becomes a challenge using HSM. This is why choosing the right HSM becomes crucial based on your use case.
For example, if you are an eCommerce business, using transactional HSM makes more sense over GP HSMs. Another essential challenge that most companies face while using HSM is scaling and resilience.
You need vendor-specific tools and technologies to integrate HSMs, making scaling harder. APi-based challenges make HSM integrations complex for many businesses. Due to hardware form, HSMs come with limited functionalities, and adding new functions becomes complex.
So, how will you overcome HSM challenges?
Here are some best practices to follow!
HSM Best Practices
- HSMs need specific operating system permissions, and that is why you need to define data access controls.
- Use subnetting or network segmentation to prevent unauthorized access to HSM
- Ensure network HSM security through firewall implementation
- Use robust TRNGs to make sure key generation
- Test HSM device through rigorous third-party inspections for better compliance with FIPS criteria
- To address scalability issues, use the master key in HSM to generate distributed keys, and wrap them in cryptographic material through an algorithm.
- Make sure you patch HSM with security upgrades regularly
- Maintain HSM security through regular hardware maintenance.
Future Trends in HSM Technology
A key trend in HSM technology will be cloud-based cryptography. Organizations are now shifting towards cloud-based HSMs to secure their digital certificates like SSL certificates and security keys. Cloud-based HSMs are also easy to scale compared to on-premise options.
Another important trend in HSM technology is the use of quantum computing. Many businesses are now focusing on quantum-resistant cryptographic security. Quantum computers have the capability of breaking robust ECC and RSA algorithms.
So, there is a focus on developing HSM technology to resist such attacks. HSMs allow the execution of such algorithms and secure communications in a post-quantum era.
Conclusion
Physical HSMs offer hardware-based acceleration, secure key management, and tamper-proof security. So, it is a great option over software-based options but there are challenges to its implementation.
Overcoming these challenges need proper testing of HSMs, using distributed strategy, and advanced algorithms. You can select the HSM suitable to your business, implement best practices and save key management costs.